In this interview given to Hicham Abed Altuab from eXtra news, Dr Carole Nakhle, CEO of Crystol Energy, discusses the notable drop in German imports from Russia and the outlook for European energy markets.
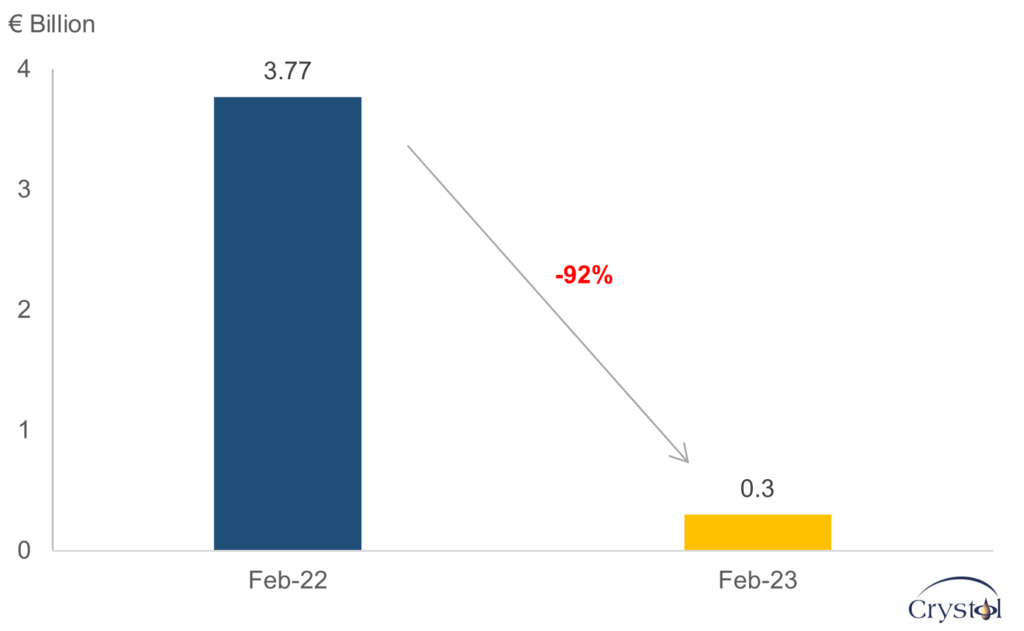
Germany's Imports from Russia
Data Source: Federal Office of Statistics, Germany
Key takeaways:
- Before the conflict in Ukraine, more than half of Germany’s gas and a third of its oil needs were met by Russia.
- The steep decline in Russian exports to Germany today is not surprising given the conflict in Ukraine and the tough stance Germany has taken against Russia.
- The decision by Germany to reduce economic and commercial relationships with Russia led to a decline in this trade by more than 90% between 2021 and 2022.
- To replace Russian fossil fuel imports, Germany strengthened its relationship with other energy exporters such as Qatar.
- The close cooperation among EU members, despite their differences, has played a major role in helping the EU to reduce the impact of the crisis.
While the conflict in Ukraine led to a rapid rise in commodity prices in Europe, namely with natural gas, it has pushed EU countries, led by Germany, to look for alternative energy suppliers as well as energy supplies (such as renewable energies).
Watch the discussion (in Arabic)
Related Analysis
“Increasing pressure on Russia’s oil industry“, Dr Carole Nakhle, Apr 2023
“Europe and Russia without Nord Stream“, Dr Carole Nakhle, Jan 2023
“Germany’s scramble to revamp its energy policy“, Dr Carole Nakhle, Oct 2022
“Russia’s oil is in long-term decline – and the war has only added to the problem“, Dr Carole Nakhle, Jul 2022
Related Comments
“Oil & gas markets outlook one year after the Russian-Ukraine conflict“, Dr Carole Nakhle, Jan 2023